Introduction
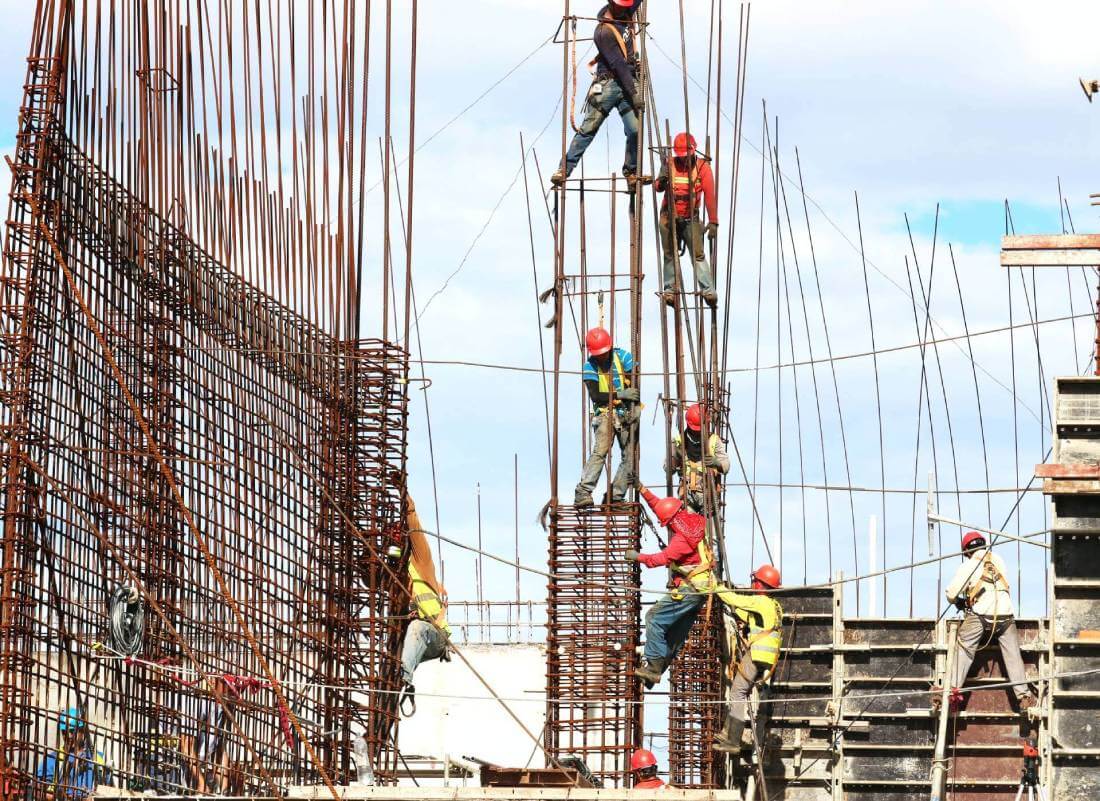
Many people have made their careers in the construction industry, or have worked in it at some point in their life. Currently, over 11 million Americans are employed by a construction company. Although construction has been an essential industry for thousands of years, construction safety is a relatively new and evolving concept. It wasn’t until 1913 when the National Safety Council was first formed to help enforce safer workplaces for construction workers. However, construction safety rules have been implemented fairly slowly.
The reality is that most construction job sites are extremely dangerous and workplace safety needs to be a top priority. To give you an idea, in 2018 it was reported that 21.1% of all workforce fatalities were in construction.
In this guide, we’re going to give you a basic understanding of construction workplace safety and how to train a smarter organization to increase safe production.
Select the best construction safety training program
What is Construction Safety?
As the name implies, construction safety involves implementing rules, regulations, and safeguards at construction sites to keep workers safe from injury and harm. There are countless hazards that could cause serious injury or death unless the proper precautions are taken.
Why is Safety Important in the Workplace?
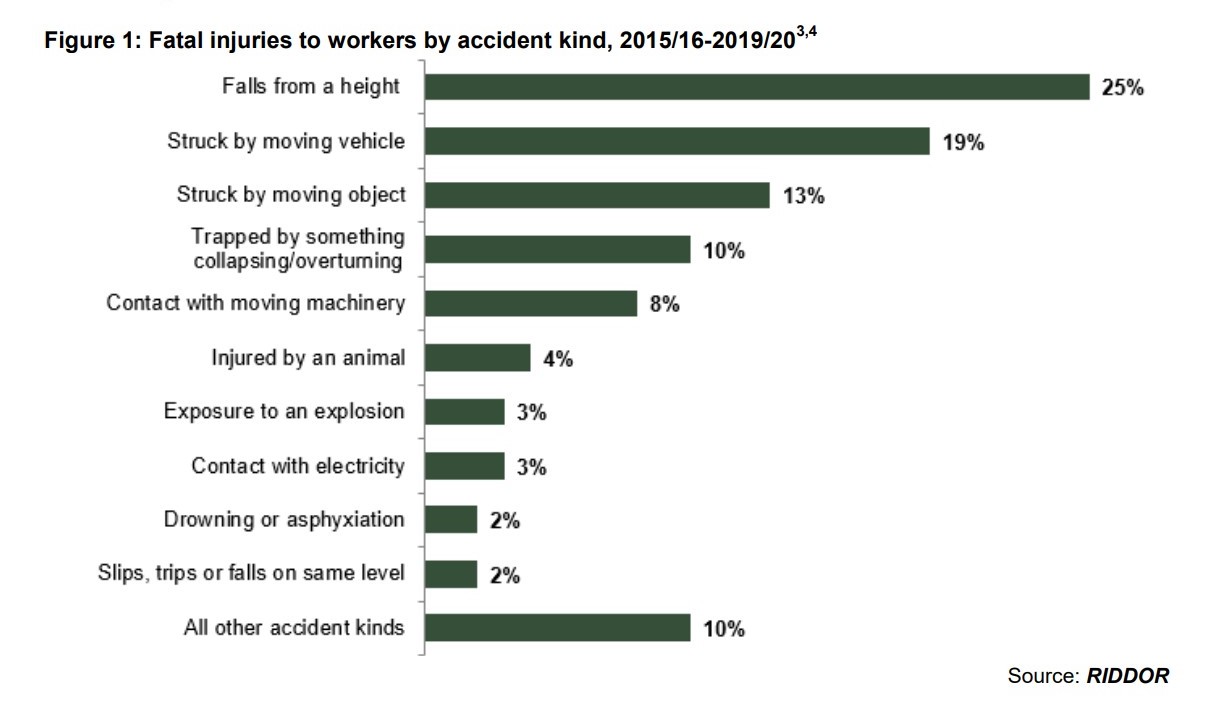
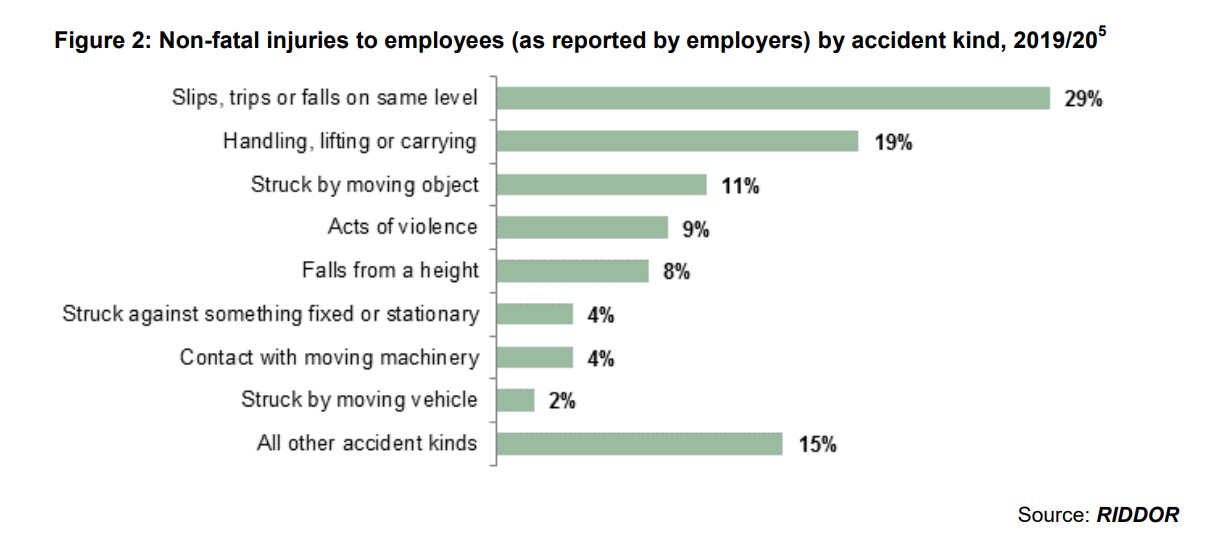
According to a recent study from the Health and Safety Executive, the majority of fatal and non-fatal injuries occurring in the workplace were related to slips and falls, collisions with objects or vehicles, or improperly moving or lifting heavy objects. Most of these injuries and fatal accidents occur in construction operations.
Implementing construction safety rules and utilizing workplace safety training helps to significantly reduce these types of injuries. These rules not only prevent dangerous accidents from occurring in the first place, but they also teach workers how to avoid dangerous situations and how to react to them.
The entire scope of workplace safety is governed by OSHA. This organization sets the rules, enforces them, and provides resources to be compliant.
What is OSHA?
OSHA stands for Occupational Safety and Health Administration. The Occupational Safety and Health Act was passed in 1970 and was created within the Department of Labor to set safety guidelines for all businesses – not just construction.
All businesses in the construction industry are subjected to OSHA compliance requirements. In order to make this possible, OSHA has issued certain regulations and directives outlining various practices for employers to create safer working environments. You can find a number of published articles on specific topics, including:
- Guidance to Compliance Officers for Focused Inspections in the Construction Industry
- Compliance Guidance for Residential Construction
- Construction Industry Outreach Training Program
- Construction Industry Quick Start
- Worker Safety Series Construction
- Scaffolding Safety
- Personal Protective Equipment
OSHA has also passed quite a bit of legislation and put many safety standards in place for the construction industry.
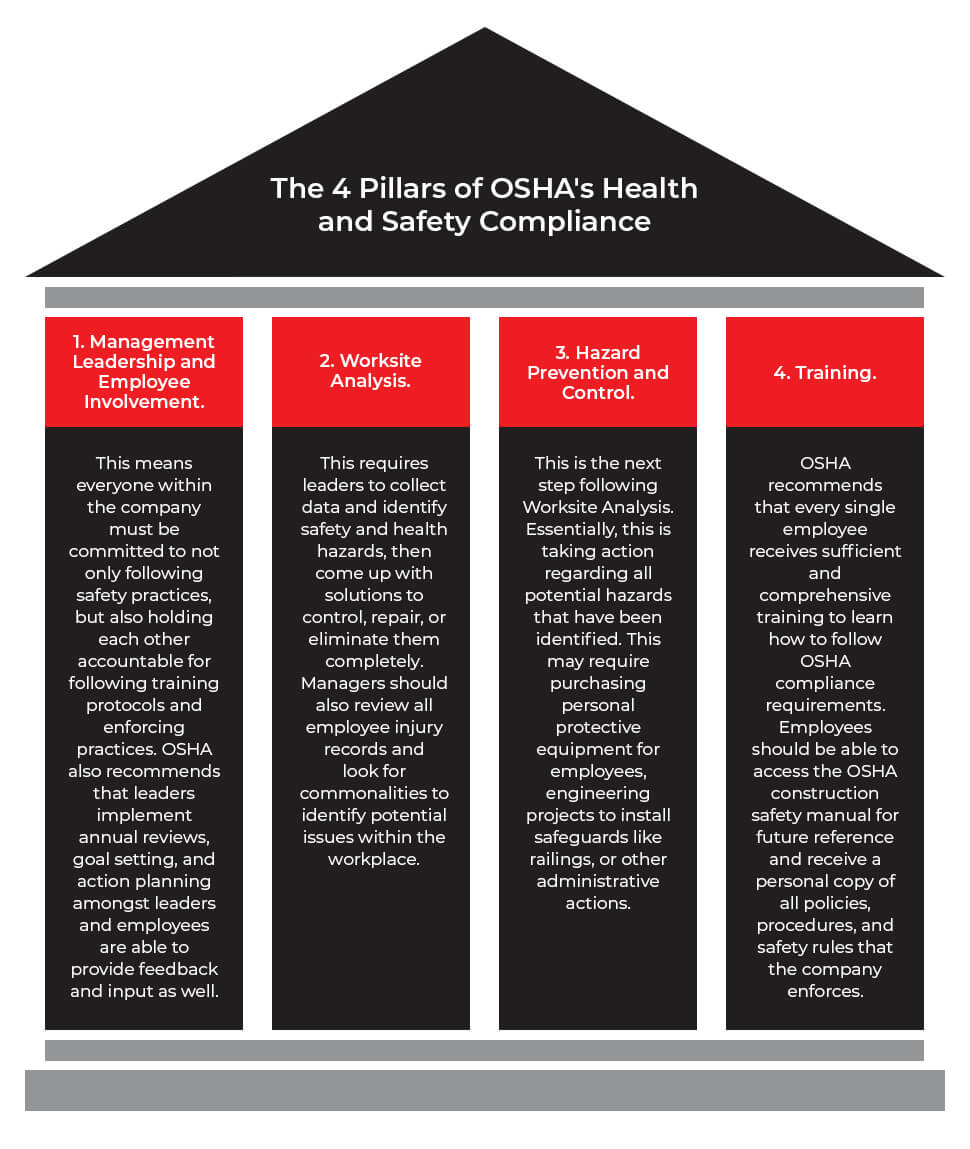
The 4 Pillars of OSHA’s Health and Safety Compliance
OSHA suggests that all employers follow their four-point safety program to instill a safer workplace. The points are as follows:
-
Management Leadership and Employee Involvement.
This means everyone within the company must be committed to not only following safety practices, but also holding each other accountable for following training protocols and enforcing practices. OSHA also recommends that leaders implement annual reviews, goal setting, and action planning amongst leaders and employees are able to provide feedback and input as well.
-
Worksite Analysis.
This requires leaders to collect data and identify safety and health hazards, then come up with solutions to control, repair, or eliminate them completely. Managers should also review all employee injury records and look for commonalities to identify potential issues within the workplace.
-
Hazard Prevention and Control.
This is the next step following Worksite Analysis. Essentially, this is taking action regarding all potential hazards that have been identified. This may require purchasing personal protective equipment for employees, engineering projects to install safeguards like railings, or other administrative actions.
-
Training.
OSHA recommends that every single employee receives sufficient and comprehensive training to learn how to follow OSHA compliance requirements. Employees should be able to access the OSHA construction safety manual for future reference and receive a personal copy of all policies, procedures, and safety rules that the company enforces.
OSHA recommends that employees receive “refresher” courses on a regular basis. Moreover, employees are taught the proper procedures for reporting any potential violations.
Construction Safety Certification
It is highly recommended that both leaders and managers (as well as the entire crew) enroll in a construction safety training program to pursue certification in specialized areas to create safer working environments.
OSHA has created workplace safety training certification courses for numerous types of topics related to construction, including:
- Aerial Boom Lift Safety
- Arc Flash Safety
- Chemical Hazards and Toxic Substances
- Construction Asbestos Awareness
- Construction Electrical Safety
- Construction Fall Protection
- Nail Gun Safety
- Crane, Derick and Hoist Safety
- Ladder and Stairway Protection
- Slips, Trips, and Falls
- Trenching and Excavation Safety
- Workplace First Aid
This allows workers – and particularly team leaders and managers – to specialize in areas where they need more experience or knowledge on topics relevant to what they do. Additionally, there are also 10-hour and 30-hour OSHA construction safety courses available covering the essentials.
Once a person completes workplace safety training, they can receive construction safety certifications. This is a certificate proving they have completed the course to the satisfaction of the instructor and are compliant with OSHA regulations.
It is important that whatever course your employees take meets OSHA’s standards for certification – otherwise, the training may not be comprehensive or accurate.
How Does Employee Safety Training Improve a Workplace?
Workplace safety training teaches workers and managers how to create safer working environments. Additionally, it educates them on ways to avoid situations which could put them and others at risk of injury or even death. Construction safety training also holds managers accountable for maintaining a safe environment – as well as enforcing rules and policies which are designed to keep workers protected.
Since the implementation of OSHA in the workplace (more on that later), the number of on-site daily fatalities has decreased from an average of 38 to 14 and injuries have been reduced from 11 accidents per day to just under 3.
What to Teach in Workplace Safety Training?
During employee safety training courses, workers are taught the proper precautions to take when operating heavy machinery, how to lift or move heavy objects correctly, and what to do if a situation is creating an unsafe working environment.
According to OSHA, workplace safety training should cover:
- 1
Fall protection
- 2
Ladder safety
- 3
Stairway safety
- 4
Trenching
- 5
Hazard communication
- 6
Heavy machinery usage policies
- 7
Personal protective equipment
Workplace training sets the precedent for the proper protocols for safety measures that must be implemented at every job site, such as reinforcements, safety railings, and protective gear that must be provided to every worker.
For bigger jobs, we recommend having safety and health professionals on staff to ensure you meet all requirements and nothing gets missed.
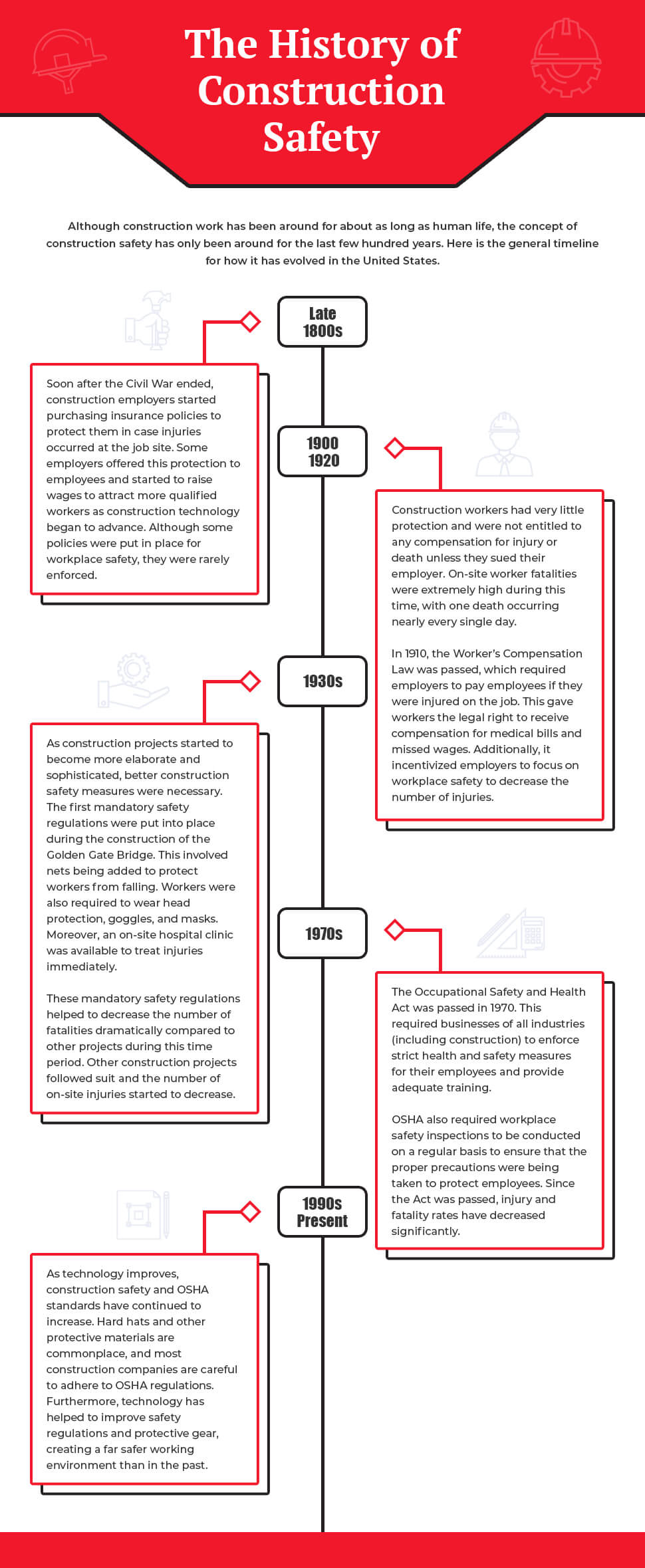
The History of Construction Safety
Although construction work has been around for about as long as human life, the concept of construction safety has only been around for the last few hundred years. Here is the general timeline for how it has evolved in the United States.
-
Late 1800s
Soon after the Civil War ended, construction employers started purchasing insurance policies to protect them in case injuries occurred at the job site. Some employers offered this protection to employees and started to raise wages to attract more qualified workers as construction technology began to advance. Although some policies were put in place for workplace safety, they were rarely enforced.
-
1900 – 1920
Construction workers had very little protection and were not entitled to any compensation for injury or death unless they sued their employer. On-site worker fatalities were extremely high during this time, with one death occurring nearly every single day.
In 1910, the Worker’s Compensation Law was passed, which required employers to pay employees if they were injured on the job. This gave workers the legal right to receive compensation for medical bills and missed wages. Additionally, it incentivized employers to focus on workplace safety to decrease the number of injuries. -
1930s
As construction projects started to become more elaborate and sophisticated, better construction safety measures were necessary. The first mandatory safety regulations were put into place during the construction of the Golden Gate Bridge. This involved nets being added to protect workers from falling. Workers were also required to wear head protection, goggles, and masks. Moreover, an on-site hospital clinic was available to treat injuries immediately.
These mandatory safety regulations helped to decrease the number of fatalities dramatically compared to other projects during this time period. Other construction projects followed suit and the number of on-site injuries started to decrease. -
1970s
The Occupational Safety and Health Act was passed in 1970. This required businesses of all industries (including construction) to enforce strict health and safety measures for their employees and provide adequate training.
OSHA also required workplace safety inspections to be conducted on a regular basis to ensure that the proper precautions were being taken to protect employees. Since the Act was passed, injury and fatality rates have decreased significantly. -
1990s – Present
As technology improves, construction safety and OSHA standards have continued to increase. Hard hats and other protective materials are commonplace, and most construction companies are careful to adhere to OSHA regulations. Furthermore, technology has helped to improve safety regulations and protective gear, creating a far safer working environment than in the past.
What Are the Top Safety Risks in Construction?
It is certainly not surprising to note that construction sites are full of safety hazards – and it unfortunately leads to around 150,000 worker injuries every year. Some of the most common safety hazards on construction sites include:
- 1
Falls
- 2
Trench Collapse
- 3
Scaffold Collapse
- 4
Electric Shock
- 5
Failure to Use Protective Equipment
- 6
Repetitive Motion Injuries
OSHA compliance regulations require construction safety rules to be enforced and provide leaders with checklists to create safer working environments that can eliminate these risks significantly. Some of the most common OSHA violations on job sites include unsafe:
- 1
Scaffolding
- 2
Fall protection
- 3
Excavations
- 4
Ladders
- 5
Head protection
- 6
Hazard communication
- 7
Training requirements
- 8
General safety and health provisions
- 9
Electrical design and protection
How to Make a Safety Plan for Construction
Establishing a company safety training program is quite a grand undertaking, especially since there are so many available topics which need to be covered. Ultimately, your safety training program needs to meet two goals:
- To properly inform and train your staff regarding the proper workplace safety protocols
- To pass the OSHA construction safety inspection
During an OSHA inspection, an inspector may walk around the entire workplace looking for potential hazards or violations. They may also conduct employee interviews regarding any concerns they have or asking questions to see how safety regulations are being implemented and followed.
At MSC Safety Solutions, we help companies set up their safety training program to be in line with OSHA requirements, as well as develop an exhaustive plan to make sure you pass the inspection, as well as develop a comprehensive plan that meets or exceeds your clients requirements.
Construction Safety Checklist
First, to create a safety training program covering everything that will be addressed in the inspection, it is important to follow the Construction Safety Checklist published by OSHA. This lays out all of the hazards you must avoid and precautions that need to be followed.
If your worksite is missing any of these components, you could receive a violation.
OSHA’s checklist includes:
-
Personal Protective Equipment
Safety glasses or shields for welding, cutting, or nailing,
Foot protection with slip-resistant and puncture-resistant work boots and safety-toed footwear to prevent injury from falling objects.
Hand protection with gloves for specific jobs, such as rubber gloves for concrete work, welding gloves, and insulated gloves for electrical hazards.
Head protection with proper hardhats to be worn at all times – and replaced if cracked, dented, or after a heavy blow. -
Scaffolding Safety
All scaffolds should have sound footing, be fully planked, and free from any hazards that could cause slips or falls. Workers should not be allowed on scaffolds during extreme weather conditions, and they should not be loaded with more weight than they are designed to support.
-
Electrical Safety
Power must be shut off when any electrical work is being done and all circuits must have an effective Lockout/Tagout system in place. Any damaged cords or cables should be replaced, all tools and equipment should be properly maintained, and electrical power lines should be at least ten feet from ladders, scaffolds, equipment, and materials.
-
Floor and Wall Openings
All floor openings must be securely covered or have a guardrail. Toe boards should be installed around the edges of permanent floor openings.
-
Elevated Surfaces
Proper signage must be posted stating surface load capacity and should be equipped with guardrails. Entries and exists must have handrails and all material piles must be stacked in a way to prevent tipping, falling, collapsing or rolling.
-
Hazard Communication
A list of all hazardous materials used in the workplace should be listed along with a written communication program regarding proper labeling and training. Each container of hazardous substances should be appropriately labeled.
-
Crane Safety
Cranes should be kept away from electrical power lines. Cranes must be equipped with load charts, load capacities, operating speed, and instructions. Only properly trained/licensed operators should be allowed to work with hoisting and rigging equipment. On job sites that involve frequent use of crane and rigging equipment, there is absolutely zero margin for error and the penalties can be great for failing essential safety inspections
-
Forklifts
Only properly trained/licensed forklift truck operators are allowed to use this equipment. Operators should be provided refresher training and evaluations. Forklifts should undergo routine inspection and meet design and construction requirements
Creating a company safety program covering the entire checklist to be OSHA compliant is a big job. We strongly recommend that construction firms hire a qualified on-site safety expert or use an online course system for OSHA construction safety training. While experts don’t come cheap, one of the biggest benefits to hiring a a construction safety consultant is nothing will slip through the cracks. Ultimately, this will save you time, stress, and money in the long run.
MSC Safety Solutions provides all of these resources to construction companies. We’ll set up your entire safety program, create checklists, policies, new hire orientation protocols, and provide a qualified expert to make sure you meet every demand of your checklist. To get the ball rolling, please review the seven ways to avoid hazards using a construction safety checklist.
Construction Risk Management
Construction risk management is an approach which helps leaders to plan, monitor, and control the measures that must be taken to prevent risks in the workplace. This involves first identifying potential hazards, coming up with ways to control the risk, and managing any residual hazards that result.
This does not necessarily include just health and safety risks.
-
Financial Risk
Factors that impact cash flow, such as unexpected cost increases.
-
Legal Risk
Factors which could prevent the fulfillment of contracts.
-
Project Risk
Hazards which could impact the success of a project by slowing things down, costing more, or require additional resources.
-
Environmental Risk
Natural phenomena which could damage construction sites, such as floods, earthquakes, or hurricanes.
Construction safety risk management takes related risks into account, such as:
- Financial risk – factors that impact cash flow, such as unexpected cost increases.
- Legal risk – factors which could prevent the fulfillment of contracts.
- Project risk – hazards which could impact the success of a project by slowing things down, costing more, or require additional resources.
- Environmental risk – natural phenomena which could damage construction sites, such as floods, earthquakes, or hurricanes.
Management teams must address these potential risks during the planning stages to find solutions and strategies to mitigate any of these situations during the building process. Your company safety program must go over all of these topics and explain why they are important to follow.
Now, it’s not always enough to just teach company safety programs, you need to enforce the lessons to avoid risk. Here are some practical ways to do this in your safety training.
Passing the OSHA Construction Safety Inspection
In order to ensure that you pass the OSHA construction safety inspection, you must be as prepared as possible and remove anything that could potentially be hazardous.
First, you must have all of your records and documentation in order. OSHA inspectors will double check that you have the proper permits, certifications, and a well-documented safety program in place. MSC Safety Solutions builds out all of these for construction companies and makes sure everyone is fully prepared for the inspection.
If any past injuries have occurred on the job site, it is important that you have records for all of these incidents, as well as:
- Hazard communication program guidebook
- Emergency preparedness and evacuation procedures
- Written lockout/tag out programs
- Respirator programs
- Exposure and medical records
- Material safety data sheets
- Bloodborne pathogen training documentation
Once an inspector arrives and gathers these materials, they will hold an opening conference to explain the purpose of the visit. They may also provide documentation if your company has received any complaints which triggered the investigation.
A manager should guide the inspector in a walkthrough of the facility. The inspector will likely be taking notes and photos or videos throughout, particularly if they notice any potential violations. The inspector may also ask employees questions during this time.
After the walkthrough, the OSHA inspector will meet with managers and company representatives to discuss any issues or violations they discovered. Some of these hazards may be resolved during this meeting. Others might require more time, so a follow-up inspection will be scheduled.
Remember that an OSHA inspection could occur at any time. It can often be a result of a complaint that has been filed. You should always be prepared for this type of inspection by creating a safe, hazard-free environment from the beginning.
How to Facilitate Proper Construction Safety Training
To best facilitate a company-wide construction safety training course, there are some strategies to help everyone retain the information more effectively.
-
Establish the Buddy System for New Hires
First, it is best to have new hires partner up with other employees to observe proper safety practices in the workplace. Typically, this should be done for the first thirty days of their employment. Then, managers should assess the new hire’s understanding of safety regulations.
-
Hold Thorough Safety Orientations for New Hires
All new hires and temporary workers should participate in a safety training program orientation session to cover essential information before they start working. This includes covering hazard recognition, policies & procedures for work conduct, as well as hazard identification & prevention.
-
Make Sure Managers Have Excellent Communication/Leadership Skills
Managers and supervisors should undergo effective and continuous training to improve their skills in hazard prevention, as well as communication skills in relation to safety. This involves refresher courses regarding skills for implementing better safety procedures and communication policies.
-
Hold Targeted Safety Training After an Incident
After any incidents – such as an on-site injury or hazard detection – managers should host team meetings to go over targeted safety training classes to discuss the topic in more detail. This is a behavior-based safety program, meaning that specific topics are covered after an incident to ensure that everyone understands how to prevent it from recurring.
Construction Safety Courses
Selecting the right construction safety training program is a key aspect in running a successful, protected operation – and consistently passing inspections. MSC Safety Solutions offers a wide variety of safety courses, including:
In addition to the above courses, we also provide NCCER training and certification. This program is designed for structural ironworkers, rigging professionals, signal persons, safety professionals, crew leaders, and project supervisors.
Check out our safety training calendar to find a program that fits your needs. For more information, feel free to get in contact with us – we are happy to guide you in selecting the training programs you need. MSC Safety Solutions offers training courses in both English and Spanish.
Conclusion
It is imperative that every employee works in an environment that is safe and hazard-free. Construction workers should also be able to access proper safety training to keep themselves and others protected – as well as know what to do in the case of an emergency.
MSC Safety Solutions is dedicated to providing thorough construction safety training covering a wide range of applicable topics. We specialize in teaching these courses in a way that is easy to understand.
If you have any further questions regarding the courses we offer or want to register, please reach out to our staff at MSC Safety Solutions for more information.